
Once you enter the mac access-list extended name command, use the following subset to create or delete entries in a MAC ACL: In systems that are configured with PFC3, if you want to classify all IPX traffic by using a MAC-access list that matches on EtherType 0x8137, use the ipx-arpa or ipx-non-arpa protocol. You can configure named ACLs that filter Internet Packet Exchange (IPX), DECnet, AppleTalk, Virtual Integrated Network Service (VINES), or Xerox Network Services (XNS) traffic based on MAC addresses (IPX filtering with a MAC ACL is supported only with a Policy Feature Card 3 ).

Must start with an alpha character and must be unique across all ACLs of all types.Maximum of 31 characters and may include a–z, A–Z, 0–9, the dash character (-), the underscore character (_), and the period character (.).When you enter the ACL name, follow these naming conventions: The following Ethertype protocol values were added to the valid protocol list: bpdu-sap, bpdu-snap, dtp, lacp, pagp, vtp. This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA. Support for this command on the Supervisor Engine 2 was extended to Release 12.2(17d)SXB. Add the ip keyword to the list of valid protocol names.Add the vlan vlan and cos value keywords and arguments.Support for this command was introduced on the Supervisor Engine 720. Global configuration (config) Command History Release Name of the ACL to which the entry belongs. No mac access-list extended name Syntax Description To remove MAC ACLs, use the no form of this command. To create an extended MAC access control list (ACL) and define its access control entries (ACEs), use the mac access-list extended command in global configuration mode. The following example applies MAC ACL 101 on incoming traffic received on Gigabit Ethernet interface 0: Router> enable Router# configure terminal Router(config)# interface gigabitethernet 0 Router(config-if)# mac access-group 101 in Related Commands CommandĬonfigures an IP access list to be used for packets transmitted from the asynchronous host.ĭisplays the ACL configuration on a Layer 2 interface.ĭisplays the contents of one or all MAC ACLs. Note The mac access-group command is supported on a VLAN subinterface only if a VLAN is already configured on the subinterface.
#Cisco mac address table default series
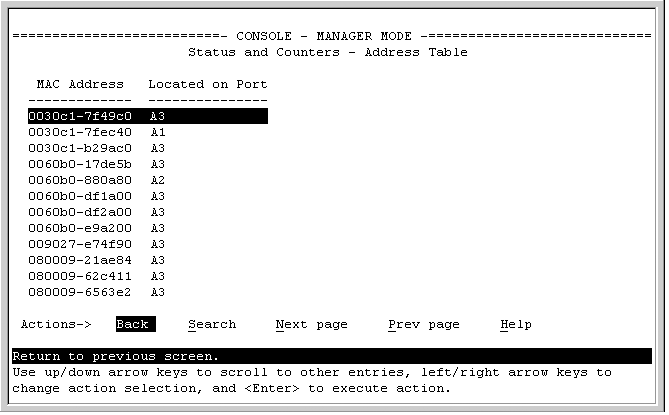
On Catalyst 6500 series switches, this command is supported on Layer 2 ports only. If the specified MAC ACL does not exist on the interface or subinterface, all packets are passed.
#Cisco mac address table default software
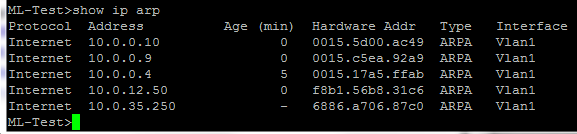
If the access list denies the address, the software discards the packet and returns an Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) host unreachable message. If the MAC access list permits the address, the software continues to process the packet. After a networking device receives a packet, the Cisco IOS software checks the source MAC address of the Gigabit Ethernet, 802.1Q VLAN, or 802.1Q-in-Q packet against the access list. MAC ACLs are applied on incoming traffic on Gigabit Ethernet interfaces and VLAN subinterfaces. This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SXH. This command was introduced on the Cisco 12000 series Internet router. Subinterface configuration (config-subif) Command History Release No access list is applied to the interface or subinterface. This is a decimal number from 700 to 799. Number of a MAC ACL to apply to an interface or subinterface (as specified by a access-list (MAC) command). No mac access-group access-list-number in Syntax Description To remove a MAC ACL, use the no form of this command. To use a MAC access control list (ACL) to control the reception of incoming traffic on a Gigabit Ethernet interface, an 802.1Q VLAN subinterface, an 802.1Q-in-Q stacked VLAN subinterface, use the mac access-group command in interface or subinterface configuration mode. pl atform port-channel local-significance.mls rp ip multicast management-interface.mac-address-table notification threshold.mac-address-table notification mac-move.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
